Biodiesel is a diesel-like fuel derived from vegetable oil or other renewable resources. It can be made from soy or canola oil, waste cooking oil, and even animal fats. Biodiesel is made by combining the vegetable oil with alcohol [usually methanol but occasionally ethanol] in the presence of a catalyst through a process called transesterification. … Read More
vegetable oil
Structure , advantages and disadvantages of Biodiesel Marke
Part 1 : Structure analysis of Biodiesel Market 1, Market environment analysis International market: In recent years, the world’s biofuel oil industry is developing rapidly. The United States, Canada, Brazil, Japan, South Korea, Australia, India and other countries are actively developing this industry. In the United States and European countries, biodiesel has been approved as … Read More
The difference between biodiesel and diesel oil
Biodiesel is a combination of biomass energy and traditional fossil energy, and can be partially regenerated. While diesel is fossil energy, it can not be regenerated. Biodiesel is a biofuel that is considered environmentally friendly, prepared from unprocessed or used vegetable oils and animal fats through different chemical reactions. This biofuel can be used like diesel. The … Read More
Biodiesel is a renewable fuel
Biodiesel is a renewable fuel made from biomass. Most U.S. biodiesel is produced from vegetable oils and animal fats. Biodiesel can be used in the same equipment as diesel fuel made from petroleum. The major sources of feedstock (raw material) for making biodiesel in the United States and their shares of total biodiesel feedstocks in 2017 … Read More
History of Biodiesel
Biodiesel was first proposed by German engineer Dr. Rudolf Diessel. At the World Exhibition in Paris in 1900, he showed his engine with peanut oil as fuel. Dr. Rudolf Diesel actually invented the diesel engine to run on a myriad of fuels including coal dust suspended in water, heavy mineral oil, and vegetable oil. His initial engine experiments were catastrophic failures. … Read More
Biodiesel and Green Diesel
The terms biodiesel and green diesel are easy to confuse and often are. Both of these products are refined from vegetable oil (and occasionally animal fat). What sets these two diesel fuels apart are the processes used to produce them and the end product that results. Biodiesel is produced by reacting triglycerides with alcohol to … Read More
Development status of biodiesel in Southeast Asia
The production of biodiesel in Southeast Asia started late, but it is growing faster. Malaysia and Indonesia, which are rich in palm oil, are the fastest-growing countries in Southeast Asia. The total crude palm oil production in the two countries accounts for about 85% of global production. There are currently about 20 biodiesel plants in … Read More
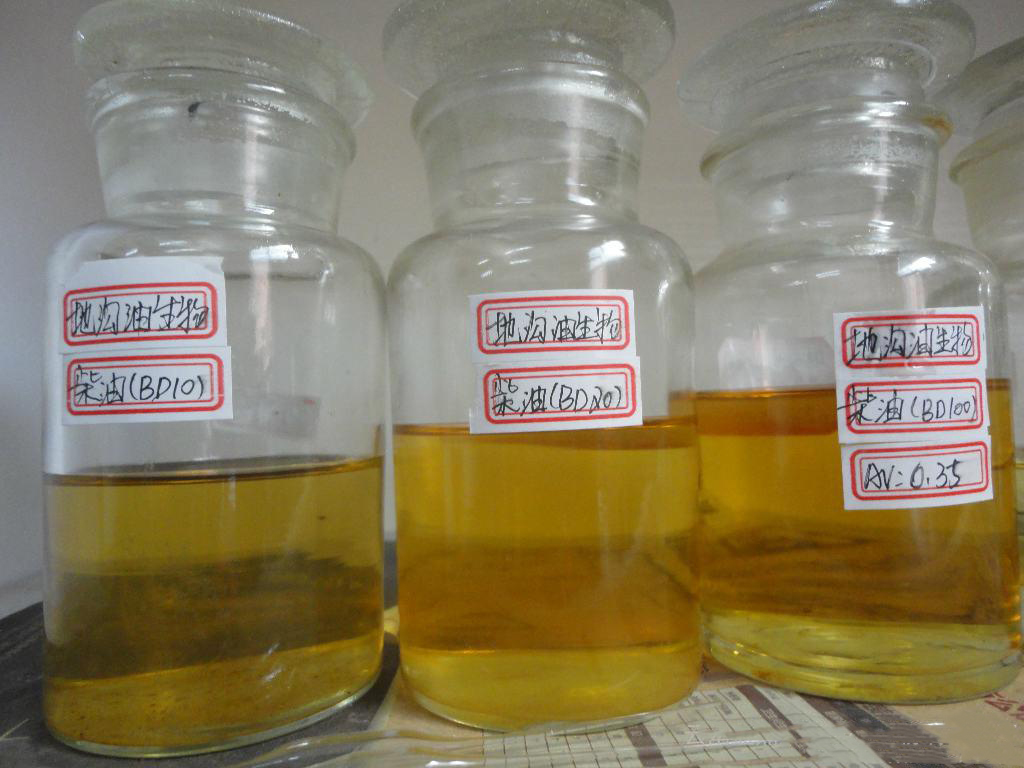
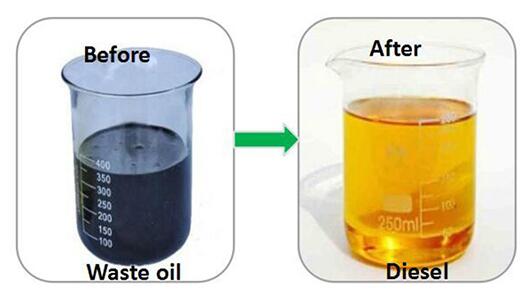
Used and Waste Oil and Grease for Biodiesel
The most environmentally friendly biodiesel feedstocks are used grease and oil. This article discussed how to turn waste oil and grease from restaurants into energy. Photo: basheertome Photo: Mitra Sahara (more information about biodiesel ,pls clink) Introduction Some of the most environmentally friendly biodiesel feedstocks are used cooking oil and waste grease. According to the EPA’s Renewable Fuel … Read More
Raw material analysis of biodiesel
“If you want to know more about oil, please click” The main raw materials of biodiesel are vegetable oil (rapeseed oil ,soybean oil ,peanut oil, corn oil ,cotton seed oil ,etc),animal oil(fish oil, lard oil, beef tallow, mutton fat,etc),wast oil or microbial oil. Biodiesel is a typical “green energy“,it has the characteristics of good … Read More
Oilseed Crops for Biodiesel Production
Do you know that energy in the oil from oilseed crops, algae, restaurant waste oil, and animal fat can serve as a biodiesel feedstock? This article explores many feedstocks that make oil, which can be used in biodiesel production. Harvesting soybeans in Nebraska. Photo: F. John Hay, Extension Educator, University of Nebraska-Lincoln Extension. Contents Oilseed Crops for … Read More